The Manufacturing Skills Crisis: A Competitive Threat
Let’s look at the numbers. According to the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM Q4 2024 Outlook Survey), 56% of leaders in manufacturing organizations cite the inability to attract and retain employees as their primary challenge. This workforce shortage is projected to worsen, with the Manufacturing Institute (2.1 Million Manufacturing Jobs Could Go Unfilled by 2030) forecasting 2.1 million unfilled manufacturing jobs by 2030. The consequences? Severe. Downtime costs Fortune 500 companies an estimated $1.5 trillion annually, according to Siemens (The True Cost of Downtime).
I love this chart. Since 1990, while labor costs have steadily increased, the cost of industrial robots has remained relatively stable, making automation an increasingly attractive option. But here’s the thing - automation has its limitations. How about where robots don’t exist yet? Like maintenance and office work? These knowledge-intensive areas remain vulnerable to skills gaps and represent significant opportunities for new solutions.
Our industry stands at a crossroads. The question is no longer whether we’ll adopt AI—it’s who will lead and who will lag behind. Companies that fail to embrace these technologies face higher costs due to inefficiencies, slower decision-making compared to AI-powered competitors, and the risk of knowledge loss as experienced workers retire. I’m seeing the gap between AI-powered manufacturers and those relying solely on traditional methods widening daily.
The Knowledge Access Problem: Why Traditional Solutions Fall Short
At the heart of our skills gap challenge lies a fundamental problem: the fragmentation of organizational knowledge. In most of our manufacturing environments, critical information is scattered across multiple systems and people:
- Equipment manuals and maintenance procedures buried in document repositories
- Valuable know-how locked in the minds of experienced technicians
- Equipment data stored in IoT systems and databases
- Business information siloed in enterprise systems like ERPs and CRMs
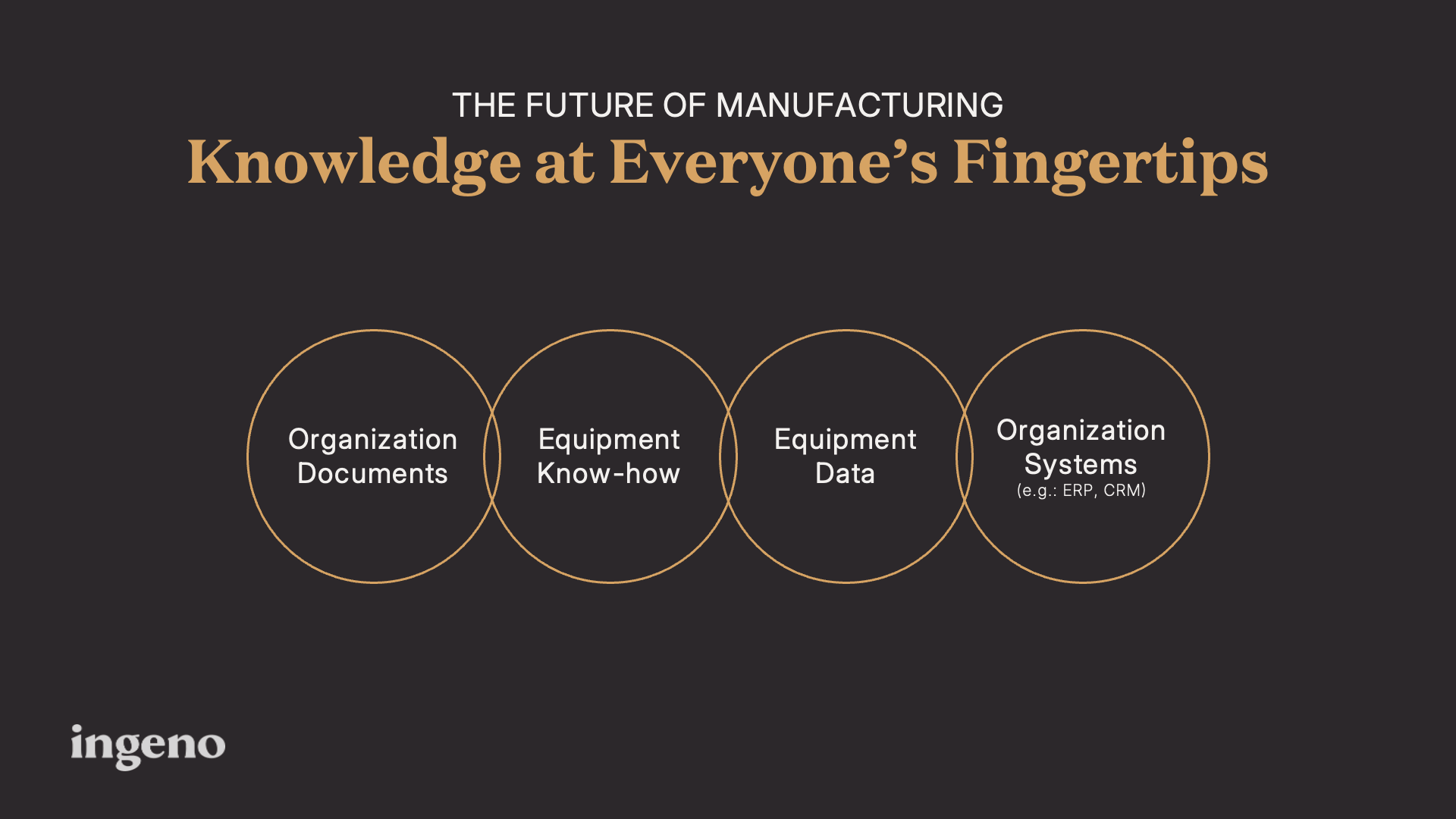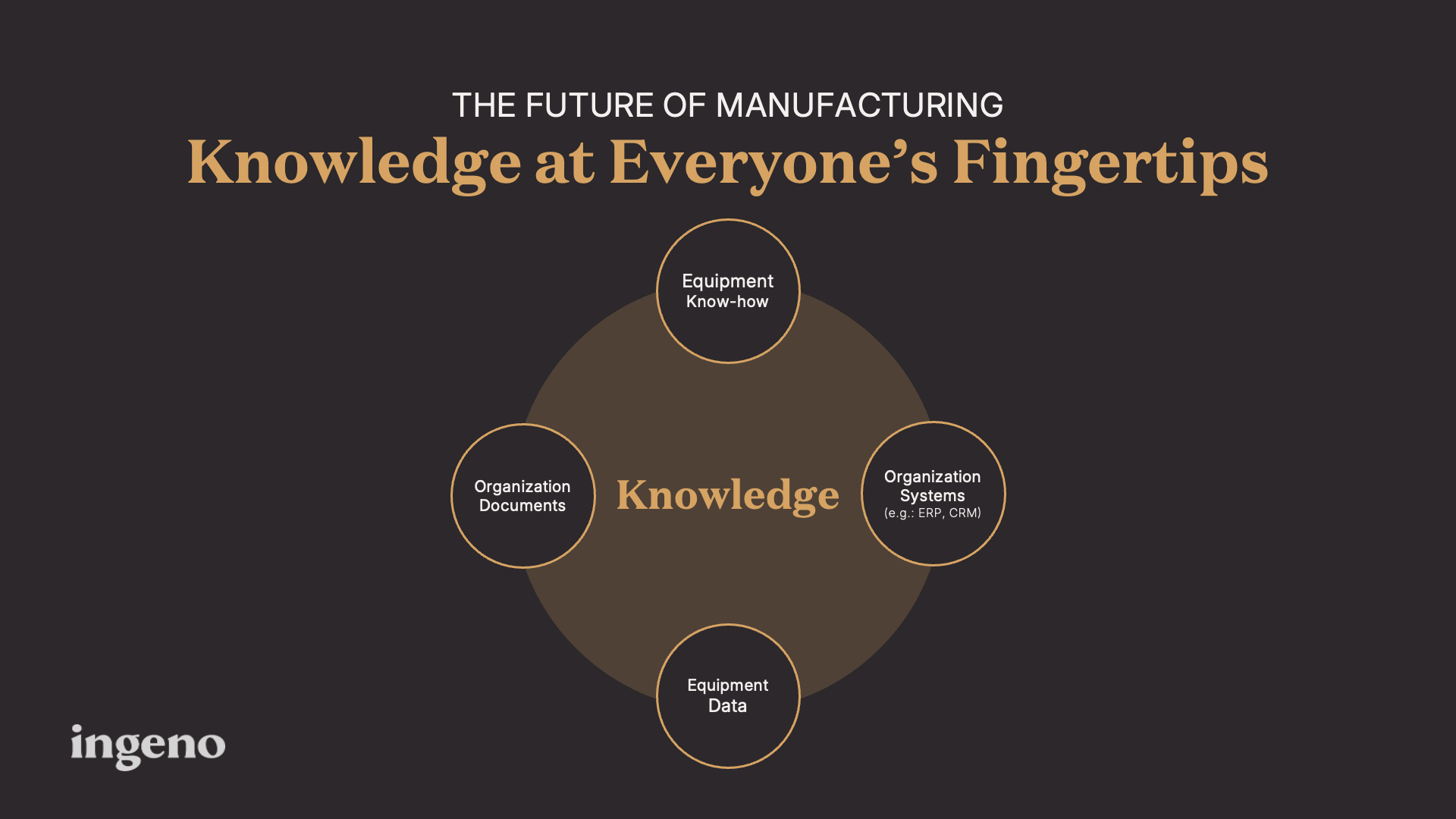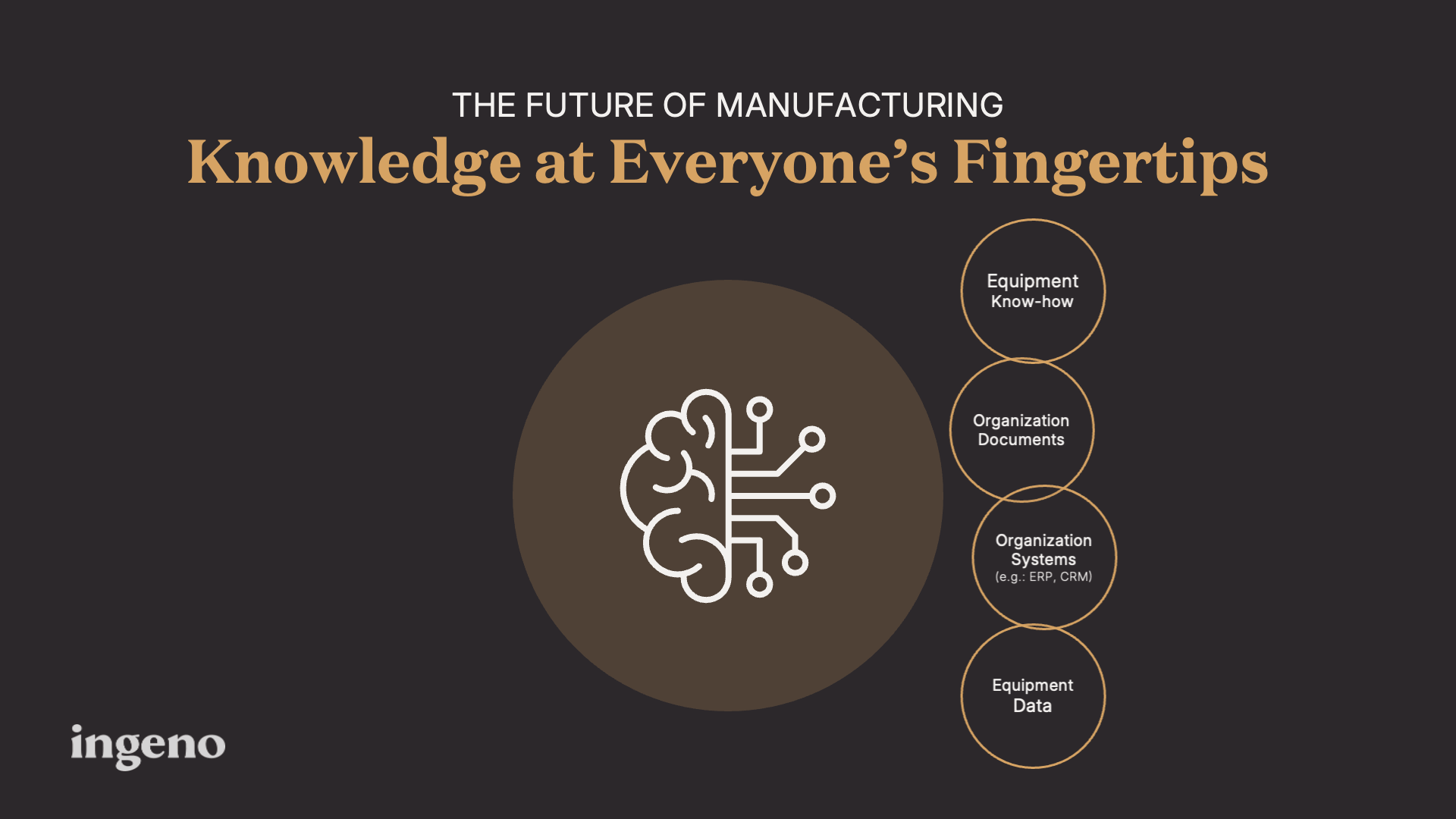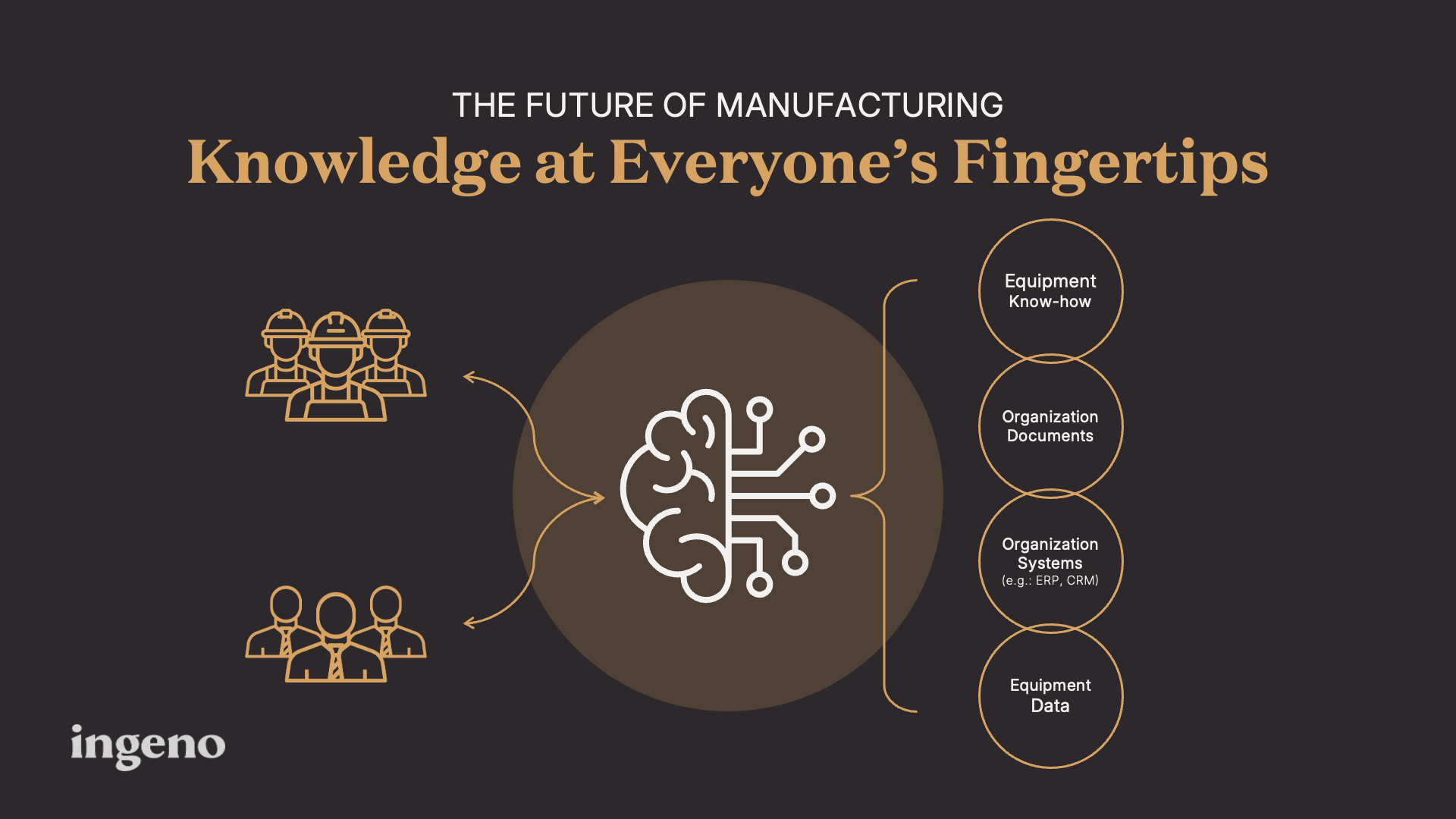
This fragmentation creates significant inefficiencies. Right now, workers waste time searching for information, troubleshooting issues, and relying on trial and error. What if relevant knowledge was at everyone’s fingertips when they need it?
Generative AI offers a transformative solution to this problem. Unlike traditional AI systems that follow rigid, pre-programmed rules, generative AI can understand context, interpret natural language, and synthesize information from diverse sources. This capability allows it to unify fragmented knowledge and make it accessible through intuitive, conversational interfaces. Workers at every level can simply ask questions and receive instant, actionable insights drawn from the organization’s collective knowledge base.
The cost of inaction is substantial. Every day without AI-powered knowledge systems means:
- Hours lost to searching for information
- Extended equipment downtime waiting for expert assistance
- Repeated mistakes due to lack of knowledge transfer
- Missed opportunities for process improvement
These inefficiencies create a competitive disadvantage that grows more significant as competitors adopt AI solutions.
Practical Applications: AI in Action Today
Let me share some compelling use cases that demonstrate how generative AI can address specific manufacturing challenges and create immediate competitive advantages:
Equipment Assistant: Streamlining Maintenance and Reducing Downtime
The Equipment Assistant helps technicians diagnose and resolve equipment issues faster by:
- Accessing contextual information - Pulling up relevant work orders, equipment details, and maintenance history
- Diagnosing problems - Analyzing symptoms and error codes against knowledge base and historical data
- Providing step-by-step solutions - Delivering clear, actionable repair instructions
- Documenting resolutions - Automatically generating detailed resolution reports
This approach dramatically reduces downtime by providing immediate expert guidance, even to less experienced technicians. The assistant becomes a force multiplier, allowing your existing workforce to solve more problems independently and efficiently.
RFP Assistant: Gaining Competitive Edge in Bidding Processes
The RFP Assistant helps proposal teams create more competitive bids by:
- Analyzing requirements - Breaking down RFP documents to identify key evaluation criteria
- Assessing competitive positioning - Comparing your strengths against industry benchmarks
- Optimizing pricing and capacity planning - Recommending strategic approaches based on market research
- Identifying risks and mitigation strategies - Suggesting approaches based on organizational best practices
This AI-powered approach gives companies a significant competitive advantage in the bidding process, ensuring proposals are more thorough, strategic, and aligned with client priorities.
Implementation Roadmap: The Imperative to Act Now
The market data is clear: generative AI investments in manufacturing are accelerating rapidly, according to research from Dimension Market Research (Europe Generative AI Market Report) and Precedence Research (Generative AI in Manufacturing Market). Companies that delay implementation risk falling permanently behind as competitors gain experience and refine their AI systems.
Implementing generative AI successfully requires a strategic approach. Here’s the roadmap I recommend:
-
Strategy & Roadmap Definition
- Problem Framing: Involve key stakeholders, clarify challenges, and prioritize critical business problems
- Solution Ideation: Define AI-driven solutions with the highest impact, leverage existing assets, and identify gaps
- Planning & Assessment: Develop an AI roadmap with concrete next steps
-
First Project Selection
- Focus on desired outcomes with clear ROI
- Identify required data sources
- Assess technical feasibility
-
Proof of Concept/Pilot Development
- Start small but with high-impact use cases
- Demonstrate value quickly
-
Learn and Iterate
- Refine based on user feedback
- Expand capabilities incrementally
-
Continuously Deliver Value
- Scale successful implementations
- Add new use cases based on proven ROI
There are several key considerations for successful implementation:
- Security: Ensure proper access control and data restrictions based on user roles
- Total Cost of Ownership: Account for development, operation, maintenance, and LLM usage costs
- Hallucination Prevention: Implement guardrails to prevent AI from generating incorrect information
- Model Selection: Choose appropriate models for specific tasks based on quality, speed, cost, and capabilities
- Data Quality & Availability: Remember that AI effectiveness depends on input data quality
- User Experience: Put users at the center of design and address change management concerns
I want to emphasize that generative AI should be viewed as an augmentation tool rather than a replacement for human workers. When someone asks, “Will this replace me?” the answer is “No, it will augment you.”
The Binary Choice: Lead or Lag
Our industry stands at the beginning of a significant transformation. Market research indicates substantial growth in generative AI investments in manufacturing, reflecting the technology’s strategic importance. For manufacturers facing skills gaps and downtime challenges, generative AI offers a powerful solution by democratizing access to organizational knowledge.
The choice is binary: either lead with AI or fall behind competitors. Early adopters are already seeing benefits:
- Reduced downtime through faster problem resolution
- Improved first-time fix rates
- Better knowledge retention as experienced workers retire
- More competitive bidding processes
- Enhanced decision-making across operations
The path forward begins with strategy development—identifying specific challenges, prioritizing use cases, and developing a roadmap. By starting with high-impact problems and taking an iterative approach, you can begin realizing value quickly while building toward a comprehensive AI strategy.
As the manufacturing skills gap continues to widen, generative AI represents not just a technological opportunity but a competitive necessity. By unifying fragmented knowledge and making it accessible to workers at all levels, manufacturers can mitigate the impact of workforce shortages, reduce costly downtime, and position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive global marketplace.
The future of manufacturing isn’t just about smarter machines—it’s about empowering people with the knowledge they need, when they need it, to perform at their best. Generative AI is the key to unlocking this future, and the time to act is now. `



